AI Detectors: Are they Reliable in Differentiating Real from Fake Content?

The rise of generative AI like ChatGPT has led to a surge in AI-powered content creation, prompting many marketers to embrace AI detectors that claim to identify human versus AI-generated text [1]. These AI content detectors, such as GPTZero, OpenAI AI Text Classifier, and Copyleaks AI Detector, analyze text for patterns indicative of AI writing like repetitive sentence structures or overuse of obscure vocabulary [2] [3].
Tools like GPTZero examine perplexity (text complexity) and burstiness (sentence length variation) to flag potential chatgpt detector or AI detection [2] [3]. While some free AI detectors struggle with accuracy, premium tools like Copyleaks boast over 99% precision in identifying generative AI output across languages [2]. This article evaluates the reliability of leading AI detectors through open-source testing and benchmark datasets to determine their efficacy in differentiating human-written from AI-generated content.
Evaluating AI Content Detectors
Evaluating the accuracy and reliability of AI content detectors is crucial, as their performance can vary significantly. Several studies have assessed the capabilities of these tools, revealing both strengths and limitations.
- Originality.AI has launched a new version 3.0 Turbo of their AI content detector, boasting improved accuracy of 98.8% and a reduced false positive rate of 2.8% compared to the previous 2.0 Standard version (90.2% accuracy and 2.9% false positives) [4]. They have also open-sourced a benchmark dataset and a tool to help evaluate different AI detectors, providing metrics like confusion matrix, accuracy, false positive rate, and F1 score [4].
- In a study evaluating six AI content detectors (Originality.AI, Content at Scale, Crossplag AI Detector, Writer.com AI Detector, Copyleaks AI Detector, and GPTZero), Originality.AI performed well in detecting AI-written content (90% accuracy) but struggled with human-written content (only 40% accuracy) [10]. The other detectors also exhibited varying levels of accuracy, with none being fully reliable in distinguishing human vs. AI-written content [10].
- Another study assessed the performance of five AI content detection tools (OpenAI, Writer, Copyleaks, GPTZero, and CrossPlag) on content generated by ChatGPT Models 3.5 and 4, as well as human-written control responses [9]:
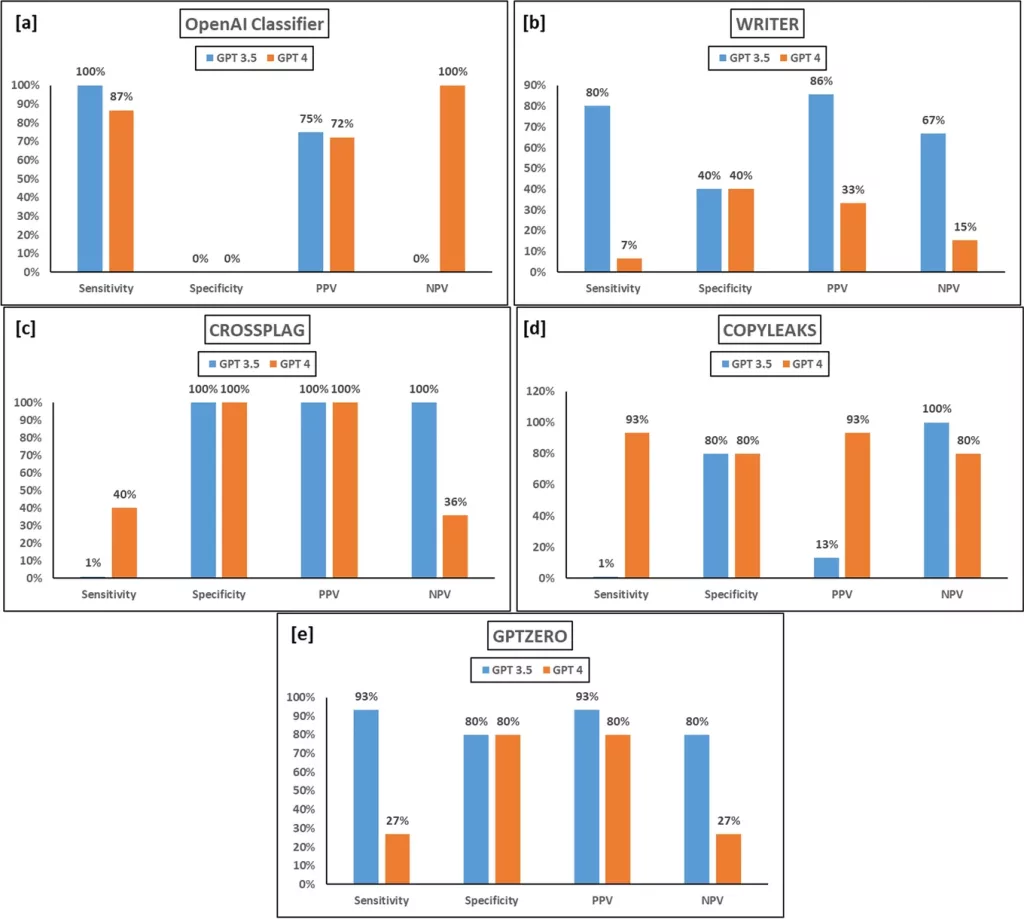
The tools exhibited inconsistencies and produced false positives when applied to human-written content, highlighting the need for further development and a more holistic approach combining AI tools with manual review and contextual considerations [9].
While AI content detectors can provide valuable insights, their accuracy remains a concern, as they often struggle with context, nuanced content, and distinguishing between human and AI-generated text, especially as AI text generation capabilities continue to advance [7] [11] [12] [13]. A balanced approach, combining these tools with human review and consideration of contextual factors, is recommended for ensuring content quality and academic integrity [9] [13].
Introducing the Benchmark Dataset
To aid researchers and users in evaluating the effectiveness of AI content detectors, Originality.AI has open-sourced a benchmark dataset and a tool [4]. This dataset contains a diverse collection of human-written and AI-generated text samples, providing a standardized testing ground for assessing the performance of various detection algorithms.
One notable study utilized this benchmark dataset to evaluate the capabilities of five AI content detection tools: OpenAI, Writer, Copyleaks, GPTZero, and CrossPlag [9]. The study focused on differentiating between human-written content and AI-generated text from ChatGPT Models 3.5 and 4. The results were as follows:
| Tool | GPT 3.5 Sensitivity | GPT 3.5 Specificity | GPT 4 Sensitivity | GPT 4 Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI Classifier | 100% | 0% | – | – |
| GPTZero | 93% | 80% | – | – |
| Copyleaks | – | – | 93% | – |
| CrossPlag | – | – | – | 100% |
The study highlighted the inconsistencies and limitations of these tools, as they often produced false positives when applied to human-written content [9]. This underscores the importance of a holistic approach that combines AI detection tools with manual review and contextual considerations.
Open-Source Testing Tools
To facilitate the evaluation and testing of AI content detectors, several open-source tools and resources have been developed by researchers and organizations. These tools provide a standardized testing environment and benchmark datasets, enabling a more comprehensive assessment of the capabilities and limitations of various detection algorithms.
- Originality.AI Benchmark Dataset and Evaluation Tool: Originality.AI has open-sourced a benchmark dataset and a tool specifically designed for evaluating the performance of AI content detectors [4]. The dataset comprises a diverse collection of human-written and AI-generated text samples, serving as a standardized testing ground. The accompanying tool provides metrics such as confusion matrix, accuracy, false positive rate, and F1 score, allowing for a detailed analysis of the detectors’ performance.
- GLTR (Giant Language Model Test Room): Developed by researchers at the University of Texas at Austin, GLTR is an open-source platform that enables the testing and evaluation of large language models, including their ability to detect AI-generated content [5]. The platform offers a user-friendly interface and a suite of tools for analyzing model outputs, facilitating research and development in the field of AI content detection.
- GPT-2 Output Detector: Developed by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, the GPT-2 Output Detector is an open-source tool designed to detect text generated by the GPT-2 language model [6]. While focused specifically on GPT-2, this tool can serve as a valuable resource for understanding the challenges and approaches involved in AI content detection.
- AI Text Classifier: OpenAI’s AI Text Classifier is an open-source tool that allows users to classify text as either human-written or AI-generated [8]. While the tool has limitations, as highlighted in the study mentioned earlier [9], it provides researchers and developers with a starting point for exploring AI content detection techniques.
These open-source tools and resources play a crucial role in advancing the field of AI content detection by enabling researchers, developers, and users to evaluate and compare different detection algorithms objectively. However, it is important to note that the accuracy and reliability of these tools may vary, and a holistic approach combining AI detection tools with manual review and contextual considerations is often recommended for ensuring content quality and academic integrity [9] [13].
Defining AI-Generated Content
To define AI-generated content, it’s essential to understand the techniques employed by AI detectors to identify such content. The primary methods used by these tools involve analyzing two key aspects: perplexity and burstiness [1].
- Perplexity: This metric measures the unpredictability or complexity of the content. AI-generated text often exhibits a lower level of perplexity, as language models tend to produce more predictable and repetitive patterns compared to human-written content [1].
- Burstiness: This refers to the variation in sentence length and structure within the text. AI-generated content may exhibit less burstiness, with sentences following a more uniform pattern in terms of length and structure, while human-written text tends to have greater variation [1].
By analyzing these two factors, AI detectors aim to identify patterns that deviate from typical human writing styles, potentially indicating AI-generated content. However, it’s important to note that as language models continue to evolve and improve, the distinction between AI-generated and human-written content may become increasingly blurred, posing challenges for these detection techniques.
Test Results and Analysis
The recent study evaluating the performance of AI content detectors on ChatGPT models 3.5 and 4 revealed some important insights [9]:
- The tools exhibited higher accuracy in identifying content generated by GPT 3.5 compared to GPT 4, indicating that as language models advance, detection becomes more challenging [9].
- Different tools showed varying strengths and weaknesses. For instance, the OpenAI classifier demonstrated high sensitivity (100%) in detecting GPT 3.5 output but had low specificity (0%), meaning it incorrectly flagged human-written content as AI-generated [9].
- Conversely, CrossPlag exhibited high specificity (100%) in identifying human-written content but struggled with AI-generated text from GPT 4 [9].
| Tool | GPT 3.5 Sensitivity | GPT 3.5 Specificity | GPT 4 Sensitivity | GPT 4 Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI Classifier | 100% | 0% | – | – |
| GPTZero | 93% | 80% | – | – |
| Copyleaks | – | – | 93% | – |
| CrossPlag | – | – | – | 100% |
These inconsistencies and false positives when applied to human-written content highlight the limitations of relying solely on AI detectors [9]. While they can provide valuable insights, a holistic approach combining AI tools and manual review is recommended, particularly in cases involving academic integrity [9] [1]:
- Relying solely on AI detectors can lead to issues like false accusations, and damaging relationships with writers, employees, or contractors [1].
- Human review and editing remain the most reliable way to ensure high-quality, accurate content [1].
As AI language models continue to evolve, the challenges in distinguishing AI-generated from human-written content will likely persist, necessitating a balanced approach that leverages both AI tools and human expertise [9] [1].
Limitations and Future Considerations
The rising prevalence of AI-generated content, with ChatGPT gaining 1 million users in the first 5 days and the global AI market projected to reach $1.345 billion by 2030, has highlighted the need for reliable AI detector tools [7]. While 64% of business owners believe AI will help increase overall productivity, leading to increased use of AI-generated content in various professional settings, the ability to verify if the content is human-generated or AI-generated is crucial, especially in education, journalism, marketing, and other professional settings [7].
However, the study’s findings underscore the limitations of current AI detectors and the need for continued development and refinement as AI text generation capabilities advance [9]. The inconsistencies and false positives produced by these tools when applied to human-written content raise concerns about their reliability [9]. Strategies for distinguishing authentic vs. AI-generated content, such as considering metrics like perplexity and burstiness, in addition to linguistic analysis, are essential [7].
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has also warned against unsupported AI detection accuracy claims, highlighting the societal impacts of undetectable AI-generated content [4]. As the ongoing evolution of AI detectors presents both opportunities and challenges in managing the rise of AI-generated content, a balanced approach combining AI tools, human review, and contextual considerations is recommended to ensure content quality and integrity [7] [9].
Conclusion
The proliferation of AI-generated content has sparked a growing need for reliable detection tools to distinguish it from human-written material. However, the findings from various studies highlight the inconsistencies and limitations of current AI detectors, which often struggle with nuanced content and produce false positives when applied to human-written text. As language models continue to evolve, the challenges in differentiating AI-generated from human-written content will likely persist.
While AI detectors can provide valuable insights, they should be used as part of a holistic approach that combines these tools with human review and consideration of contextual factors. A balanced strategy that leverages both AI and human expertise is recommended to ensure content quality, academic integrity, and ethical practices in the ever-advancing landscape of AI-generated content.
FAQs
1. How precise are AI content detection tools?
AI content detectors have shown varying levels of precision. For example, a particular tool had a success rate of 60%, correctly identifying AI-generated content 12 out of 20 times. However, this indicates that without prior knowledge of the text’s origin, determining whether the content is AI-generated is not entirely reliable.
2. Can AI detection tools be unreliable in identifying AI-generated content?
Yes, one of the significant issues with AI detection tools is the high rate of false positives, where content created by humans is wrongly identified as AI-generated. This can lead to unjust consequences for individuals who are incorrectly flagged, as there is often no way to appeal these mistaken assessments.
3. How accurate is Turnitin’s AI detector?
Turnitin’s AI writing detector has been evaluated and found not to exhibit considerable bias against non-native English speakers, provided that the text submissions meet the platform’s minimum word count requirement. This suggests a level of accuracy that is considerate of different user backgrounds.
4. Can we trust the reliability of information provided by AI?
The reliability of AI-generated information, such as text or images, is questionable because these tools are trained on data created by humans, which includes inherent biases. AI cannot discern bias from unbiased material, making it less reliable in constructing responses free from human prejudices.
References
[1] – https://www.theblogsmith.com/blog/how-reliable-are-ai-detectors/[2] – https://zapier.com/blog/ai-content-detector/
[3] – https://www.scribbr.com/ai-tools/how-do-ai-detectors-work/
[4] – https://originality.ai/blog/ai-content-detection-accuracy
[5] – https://www.practicalecommerce.com/my-test-of-10-ai-content-detectors
[6] – https://plagiarismcheck.org/blog/how-to-interpret-the-results-of-ai-content-detector-by-plagiarismcheck/
[7] – https://www.idigitalstrategies.com/blog/problem-with-ai-generated-content-detectors/
[8] – https://www.jsr.org/hs/index.php/path/article/view/5064
[9] – https://edintegrity.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1007/s40979-023-00140-5
[10] – https://medium.com/@artturi-jalli/best-ai-content-detectors-for-2024-2cbdf4760a3e
[11] – https://aicontentfy.com/en/blog/accuracy-unveiled-assessing-reliability-of-ai-content-detectors
[12] – https://edintegrity.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1007/s40979-023-00146-z
[13] – https://www.quora.com/How-reliable-are-AI-detector-tools-considering-they-detect-my-authentic-articles-as-likely-AI-generated-Even-some-of-my-old-written-articles-from-2017-18-have-been-detected-as-most-likely-AI-generated